Breast Augmentation vs. Breast Lift
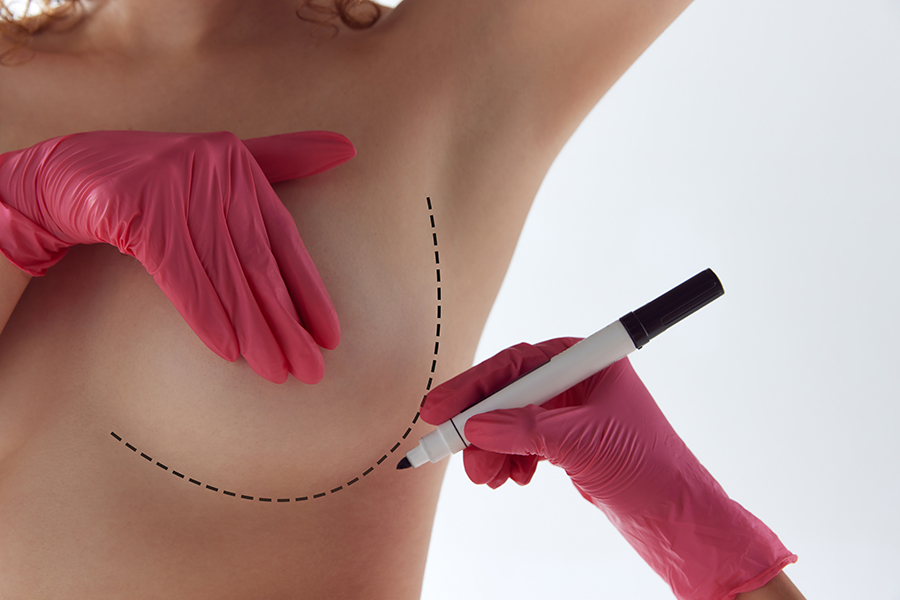
Surgical breast procedures have become increasingly popular choices for women seeking to enhance the appearance of their breasts. Two commonly opted-for procedures are breast augmentation and breast lift, both falling under the umbrella of aesthetic breast surgery.
While both procedures aim to improve the overall shape and appearance of the breasts, they serve different purposes and involve distinct techniques.
Breast Augmentation
Breast augmentation, a widely performed surgical procedure, primarily focuses on increasing breast volume and achieving a fuller bust. The procedure involves the placement of implants, which may be saline or silicone, to augment the size of the breasts. Women often opt for breast augmentation to address concerns such as asymmetry, loss of volume due to pregnancy or weight loss, or simply to achieve a more proportional and voluptuous silhouette.
Procedure Overview
- Consultation: Before the procedure, a thorough consultation with a qualified plastic surgeon is crucial. The surgeon assesses the patient’s goals, medical history, and current breast anatomy to determine the most suitable approach.
- Incision and Implant Placement: Breast augmentation involves making an incision, typically in the crease beneath the breast, and placing the implant either behind the breast tissue or under the chest muscle.
- Recovery: Recovery time varies, but patients can usually resume normal activities within a week, with full recovery taking a few weeks.
Breast Lift
On the other hand, a breast lift, also known as mastopexy, is geared towards addressing sagging or drooping breasts. It can also be a method of breast reshaping. This condition may result from factors such as aging, pregnancy, or significant weight loss, leading to a loss of skin elasticity. Unlike breast augmentation, a breast lift does not involve adding volume but rather reshapes and elevates existing breast tissue for a more youthful appearance.
Procedure Overview
- Evaluation and Planning: A comprehensive evaluation is conducted during the initial consultation to assess the degree of breast sagging. The surgeon then formulates a personalized surgical plan.
- Incision and Tissue Reshaping: The breast lift procedure typically involves making incisions around the areola and, in some cases, extending vertically down to the breast crease. Excess skin is removed, and the remaining tissue is reshaped to achieve a more lifted contour.
- Recovery: Recovery from a breast lift may require more time compared to breast augmentation. Patients can usually return to normal activities within two weeks, with full recovery taking several weeks.
Comparative Analysis
Purpose and Goals
- Breast Augmentation: Primarily focuses on increasing breast volume and enhancing overall breast size.
- Breast Lift: Concentrates on correcting sagging breasts, restoring a more youthful and lifted appearance.
Incisions
- Breast Augmentation: Involves incisions typically made in the breast crease, resulting in minimal scarring.
- Breast Lift: Requires incisions around the areola and, in some cases, vertically down to the breast crease, potentially resulting in more noticeable scars.
Implants
- Breast Augmentation: Involves the use of implants (saline or silicone) to achieve the desired increase in breast volume.
- Breast Lift: This does not involve the use of implants; rather, it reshapes existing breast tissue and removes excess skin.
Recovery Time
- Breast Augmentation: Generally has a shorter recovery period, with patients resuming normal activities within a week.
- Breast Lift: Requires a longer recovery period, with full recovery taking several weeks.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between breast augmentation and breast lift hinges on individual goals and concerns. While breast augmentation is ideal for those seeking increased volume and fullness, a breast lift is tailored to address sagging and achieve a more lifted contour.
